Successful Case: Conveyor Structural Evaluation
Kot has carried out a structural evaluation study for a belt conveyor contained in a maritime terminal. In order to do so, a static and component’s connection analysis took place following the due standards. Read this article to learn more about this success story developed by the company’s team!
You can also read more cases performed by KOT Engenharia here!
Introduction
Belt conveyors are equipment widely used for bulk material handling. Its applications can attend to various demands.
KOT has developed a study which aimed at performing a structural analysis of these assets, through static and connections analysis. Figure 1 presents a design view of these structures.

To avoid sea contamination due to falling material, fall protection structures were designed for the belt conveyors the structural study carried out considered the increase in load caused by these additional structures.
Structure modeling
Starting the study, the first stage performed as the carrier modelling in elements related to beam-column with the help of the analysis program based on the Finite Elements Method (PROCAL 3D), developed by the company, aiming to determine the effort and acting tensions and thus, allowing the structural analysis in regards to the concerning standards.
In order to assist the computational model, a tridimensional structure was rendered through the coding language VRML, as can be seen on Figure 2.

Load definition
The next stage of the project defined the applicable loads to be used in the analysis in accordance with the ASCE 7-05 [2] and NBR 8800:2008 rules [3]. Some of the considered loads were:
- Self weight;
- Material load;
- Belt tension;
- Overload on the walkways and crossover stiles;
- Wind-related load;
- Transfer chute clogging.
The criteria used for the evaluation of the bar elements that was used in the structure are presented as follow:
- Safety factor: assesses the degree of request to which a structural element is being submitted. It is determined starting with the relationship between acting effort over a bar and the permissible resistance determined by standard on metallic structures;
- Static safety factor: is the value defined by standard, used as a reference for the approval or rejection of the request degree of a structural element.
The static safety factor for a bar element, for all the potential loads is considered 1.
Connections analysis
The connection elements promote an union between the structural parts themselves or with external elements. As means for said connections, it is possible to use welding, screws, threaded bars and pins.
All the connections are classified according to its hardness, that is, its ability to prevent the relative rotation of connected parts. Two categories are possible according to this criteria:
- Simple connection: does not present resistance to bending moments. In this case, only normal and shearing effort transmission occurs;
- Moment connection: is characterized by the complete restriction of the bending moments. In this case, it does not present considerable relative rotation after loading the application.
These connections must be dimensioned in such a way that its resistance calculations are the same or higher than the required connection, withstanding all the acting actions and satisfying all the requirements presented at the NBR 8800: 2008 [3].
The criteria used for the verification of the connections is shown:
- Safety factor: represents the requirement degree to which the connection is being submitted. The connection is approved when its factor is inferior to 1.
Results
The static analysis of the carrier was accomplished aiming to determine the impact of the installation of the fall protection structures. Thus, three diverse scenarios were considered and are detailed below.
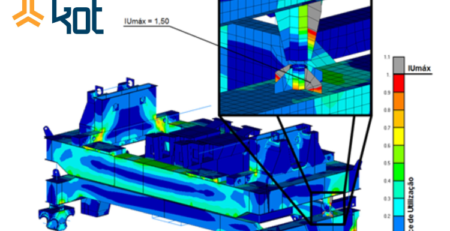
1st – Material clogging: for this structure verification, the usage indexes obtained are presented on Figure 3.
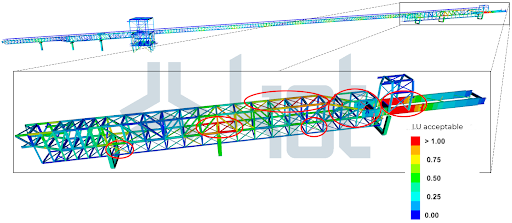
As can be seen in the Figure, some elements failed in the analysis.
2nd – Boundary condition: the main objective is to determine the structure’s boundary conditions, i.e. what is the material maximum load in the fall protection structures. The result can be seen on Figure 4.
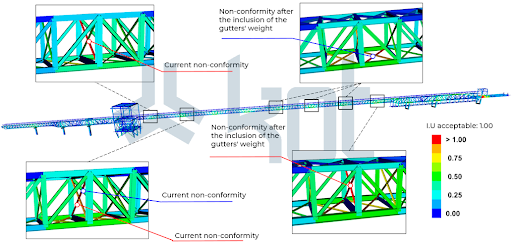
Thus, it was concluded that the structure was not prepared for the fall protection structures installation and reinforcements are required.
3rd – Average fall protection structures operation: the main objective of this analysis is to highlight the elements which require structural reinforcement to ensure a successful installation of the fall protection structures. Figure 5 shows the results achieved at this final stage of the analysis.
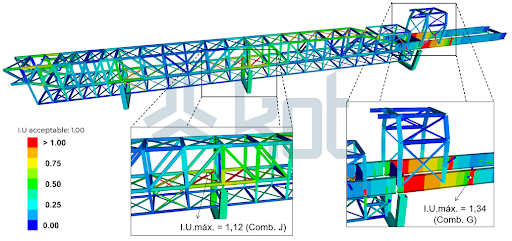
During the static and connections analysis, it was possible to ascertain that the structure was not ready for the fall protection structures installation without considering further modifications. Thus, KOT suggested some required actions to ensure the structural integrity of the assets.
Conclusion
Even though the solution for the material fall protection structures was acceptable under an environmental analysis, the structural study acted in order to mitigate risks of structural collapse by proposing improvements which should have been addressed before the implementation of this containment system.
At this point it is crucial to emphasize that KOT has a high contingent in the know-how area, having dealt with over a hundred belt conveyors calculations, thus being also able to evaluate different operational contexts and contribute with results specifically tailored for our clients.
Get in touch with KOT’s specialists team!

KOT Engenharia’s Team
With over 29 years of history and various services provided with excellence in the international market, the company promotes the integrity of its clients’ assets and collaborates in solutions to engineering challenges. For this integrity, it uses tools for calculation, inspection, instrumentation and monitoring of structures and equipment.
References:
[1] Kot Engenharia’s Archives
[2] AISC 2005 – Specification for Structural Steel Buildings, Allowable Stress Design and Plastic Design, July 2006, American Institute of Steel Construction.
[3] ABNT, NBR 8800, Projeto de estruturas de aço e de estruturas mistas de aço e concreto de edifícios, 2008;









Leave a Reply