O conhecimento das acelerações e vibrações atuantes em um ativo é essencial para o planejamento de ações de manutenções preditivas, planejadas, preventivas e, em casos extremos, corretivas nas máquinas e estruturas. Essas ações podem otimizar a integridade estrutural do equipamento quando realizadas de forma assertiva.
O método dos elementos finitos pode simular o comportamento dessas máquinas e estruturas quando submetidos a essas acelerações e vibrações. Ainda que uma estrutura seja aprovada do ponto de vista estático, o comportamento dinâmico poderá ocasionar eventuais colapsos estruturais em função da frequência de vibração dos equipamentos oscilatórios. Para obter essas frequências é possível utilizar equipamentos capazes de mensurar dados vibracionais, como câmera/sensores e acelerômetros.
The aim of this article is to present, in detail, the use of accelerometry to analyze vibrations and dynamics in structures.
What is the accelerometer?
In short, an accelerometer is an electronic sensor that can be attached to the surface of an object of study from which you want to collect acceleration and vibration data. This makes it possible to determine the body's position in space as a function of time [1]. One of these sensors can be seen in Figure 1.

Figure 1: Accelerometer [2]
The accelerometry method consists of instrumenting the asset with accelerometers at strategic points, connected to a data acquisition system which is responsible for electronically recording the information collected. To identify the points where the sensors are to be installed, a preliminary study is carried out to map the points most susceptible to variations in acceleration and vibration values.
An acquisition system commonly used in this type of test can be seen in Figure 2. Once the data has been collected, computer processing is carried out to refine the values found. These values can then be inserted into the computer model for structural verification.

Figure 2: Compact data acquisition system. [2]
Mass-spring system
The basic principles of an accelerometer come from the physical system of a mass coupled to a spring, known as a mass-spring system. This is a harmonic oscillator that restores its initial position from the force stored in the spring when it is removed from its original state by an applied force. Figure 3 shows a schematic of this system.

Figure 3: Schematic of a mass-spring system. [2]
The equation for this movement is obtained from Newton's second law and is illustrated in Equation 1, where damping forces have been applied. These forces can come from air resistance, friction or other dissipative effects.
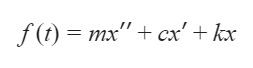
Equation 1: Calculation of force as a function of time.
Where:
- f (t) = force as a function of time;
- m = mass of the system;
- x'' component of the acceleration;
- c = damping coefficient (varies mainly according to air resistance and friction);
- x' = velocity component;
- k = spring stiffness;
- x = displacement of the mass in relation to its equilibrium point.
This model is highly relevant to the study of natural phenomena, as it generates acceptable results for studies of small movement amplitudes.
De forma análoga ao sistema massa-mola, a massa presente no acelerômetro causa deformações nos materiais piezoelétricos, internos do sensor, que atuam como extensômetros, gerando uma carga elétrica proporcional à deformação existente. Com a massa interna constante e a deformação gerada, proporcional à carga elétrica, é possível, então, calcular a aceleração do corpo.
Accelerometry applications
As frequências naturais em teoria dependem apenas da massa e rigidez do sistema, o que faz com que seja possível fazer as análises modais com essas informações. Essas análises consistem em estudos por meio do método dos elementos finitos para compreensão das respostas estruturais frente aos modos de vibração naturais do objeto. Porém, nem sempre os dados disponíveis são os reais e, em alguns casos, não existem informações disponíveis. Assim, pode-se realizar a instrumentação de um ativo com acelerômetros para calibração do modelo computacional.
Due to the characteristics of the equipment, it is common to use accelerometry in vibrating equipment such as screens and crushers, as well as in the buildings and structures that receive such equipment.
Para o estabelecimento da integridade estrutural desses ativos é fundamental realizar as análises dinâmicas aplicáveis. Caso a frequência de operação de uma máquina seja igual a sua frequência natural, ocorrerá o fenômeno de ressonância, que amplifica as vibrações e pode culminar em falhas prematuras.
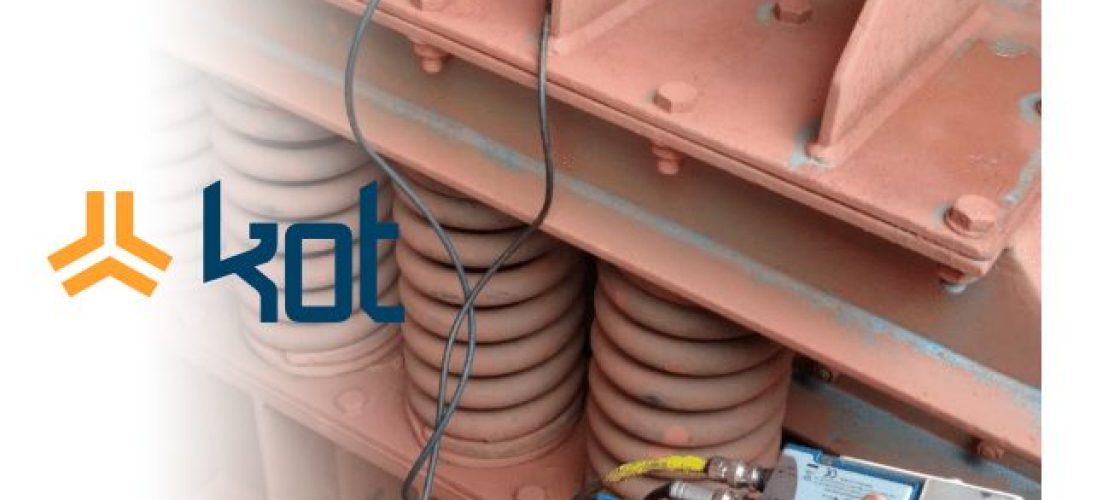
Figure 4 shows an example of vibration measurement at the base of a sieve, in an area close to the spring, showing the locations where the accelerometers were attached.
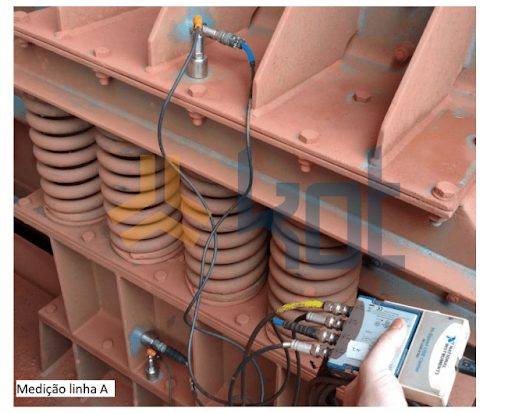

Figure 4: Example of typical attachment points used in vibration measurement. [2]
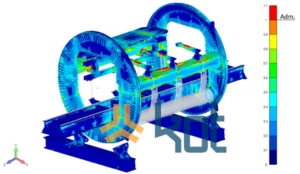
The results of the accelerometry activity were used to feed the finite element model of the base of the building in which the screens are inserted and Figure 5 shows the modal analysis of the structure for a given natural frequency.
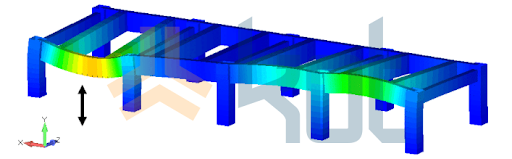
Figure 5: Result of the modal analysis of the sieve structure and support. The data collected by accelerometry is used to feed the computer model.
Caso deseje conhecer mais sobre Análise de Vibrações e Dinâmica de Estruturas confira o artigo da Kot sobre o tema clicando aqui!
Conclusion
Embora estruturas e equipamentos possam não apresentar problemas em seu comportamento estático, é necessário verificar as frequências naturais de vibração para evitar o fenômeno de ressonância que pode levar ao desgaste e falha prematura dos componentes do sistema. A Kot possui grande experiência em análises dessa natureza, podendo avaliar diferentes condições e cenários de estudo em diversos equipamentos oscilatórios. Para conhecer mais sobre as aplicações e quais são as necessidades para os ativos da sua empresa, entre em contato com a equipe da Kot!
Siga também nossas páginas no LinkedIn, Facebook e Instagram para continuar acompanhando nossos conteúdos.
Referências
[1] Jost. D. (2019/07/11). What is an accelerometer?. Disponível em: <https://www.fierceelectronics.com/sensors/what-accelerometer>
[2] Kot Engenharia Collection.